Our world has existed for approximately 4.5 billion years and humanity has been inhabited in our world (Göbeklitepe) for approximately 12,000 years. As I mentioned in my previous articles, our Earth is in a natural location within our Solar System and life is possible because it is in the Goldilocks zone. However, the issue that various space agencies have been thinking about in recent years is the question of What Happens If an Asteroid Hits Our Earth? Although many articles have been written on this subject, let’s analyze together what will actually happen.
A large meteor hitting the Earth is an event that occurs quite frequently on the geological time scale. While small meteorites burn up in the atmosphere and become ash, larger meteorites can reach the earth and cause damage. The last major impact occurred 66 million years ago when the asteroid Chicxulub hit the Earth and caused the extinction of the dinosaurs. Scientists are tracking meteorites that have the potential to hit the Earth. These meteors are called “Near Earth Objects” (NEO). On NASA’s website https://cneos.jpl.nasa.gov/ca/ it is possible to track NEOs currently in near-Earth orbits and at risk of collision.
The asteroid currently at highest risk of hitting Earth is 2023 RQ2. This meteorite is about 60 meters in diameter and will pass very close to Earth in 2046. Although the probability of impact is very low (about 1 in 1600), this asteroid could cause major damage if it hits Earth. Scientists continue to develop new methods to detect and track NEOs that could potentially pose a threat to Earth. Spacecraft are also being developed to detect and deflect a NEO should it hit Earth.
Asteroid Impact on Earth: Possible Consequences
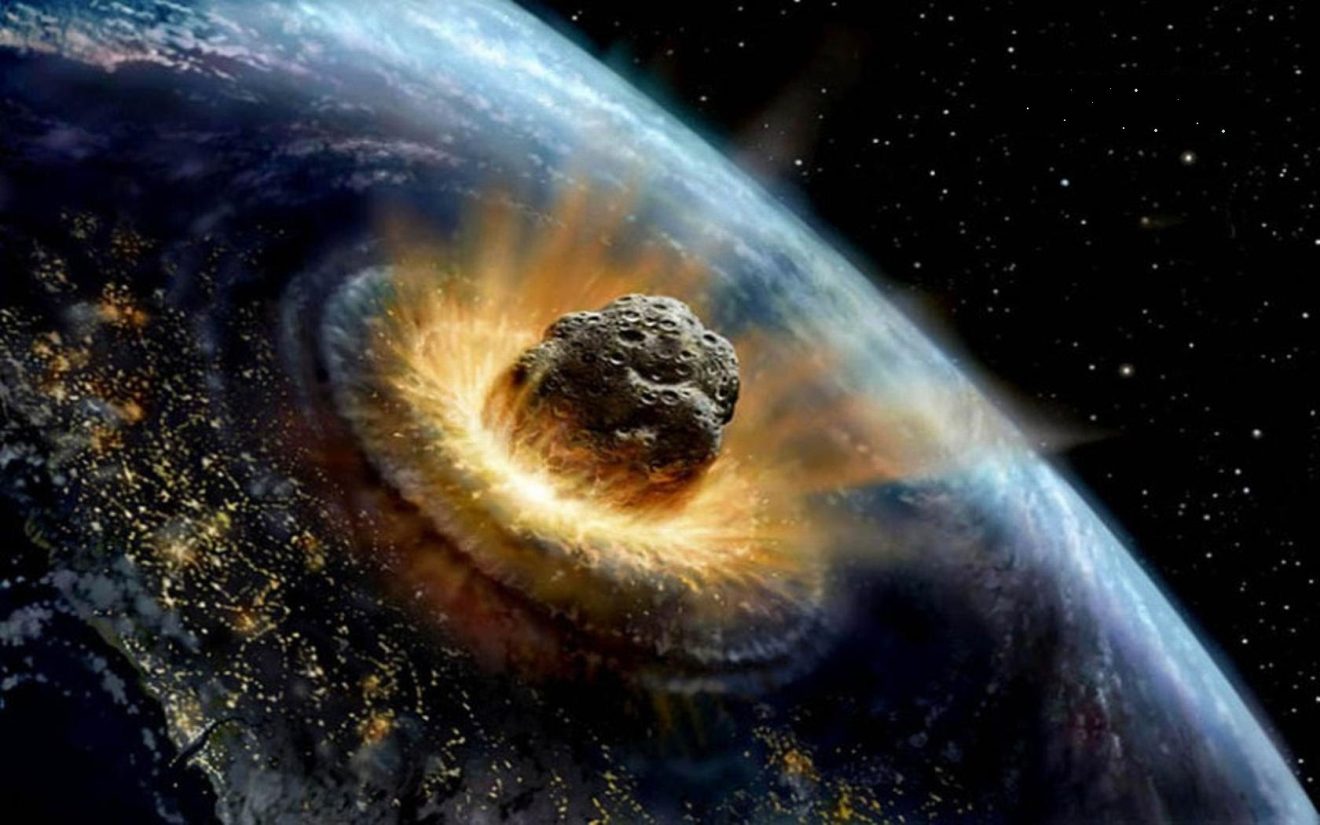
A large meteorite impacting the Earth is an event that, although extremely rare on the geological time scale, can have extremely devastating consequences. Factors such as the size of the meteorite, its composition and impact speed determine the severity of the effects. The events that will occur if a large asteroid hits the Earth will vary depending on the size, speed and impact point of the collision. But overall, the effects of such an event would be quite devastating and far-reaching. The impact of a large asteroid can trigger a range of direct and indirect effects.
Catastrophic Impact Explosion
First of all, when the moment of impact of the meteorite and its immediate aftermath are examined, a huge explosion occurs at the point of impact. This explosion releases energy many times greater than that of nuclear bombs. As a result of the impact, a large crater is formed and all life forms around this crater instantly disappear. The explosion also creates massive shockwaves and fireballs. Shock waves can cause massive destruction even in areas thousands of kilometers from the point of impact. Buildings collapse, forests topple and huge fires start. Following the impact, large amounts of dust and debris rise into the atmosphere. These particles block sunlight and can trigger a phenomenon known as “nuclear winter.” The decrease in sunlight causes global temperatures to drop and photosynthesis to stop. Vegetation rapidly declines, leading to mass die-offs of plant-eating animals and the carnivores that follow them. Global ecosystems collapse and food chains are broken.
Asteroid Impact leadıng to Tsunamis
A meteorite hitting the sea can also cause huge tsunamis. These tsunamis hit coastlines and move inland, threatening the lives of millions of people. Water resources are polluted, infrastructure is destroyed and large-scale migrations begin. Coastal ecosystems and marine life are also greatly damaged. In the weeks and months immediately following the impact, secondary disasters such as fires and acid rain occur. Forest fires cover large areas, causing more carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases to be released into the atmosphere. This could further exacerbate climate change in the long term. Acid rain pollutes water resources and damages vegetation.
Collapse of Economic Systems
Their impact on human civilization will also be great. Economic systems collapse, agriculture and industry come to a halt. Healthcare systems struggle to cope with rising injuries and disease outbreaks. Social order breaks down and competition over resources increases. During this period, humankind’s struggle for survival once again reveals the importance of social solidarity and international cooperation. In the long term, it can take years or even decades to recover from the effects of a collision. As dust and debris slowly settle in the atmosphere, sunlight begins to reach the earth again and vegetation slowly recovers. However, biodiversity may have been severely reduced and many species may have disappeared completely. While human communities try to rebuild the destroyed infrastructure and establish a new order, technology and scientific knowledge gain great importance in this process.
As a result, the effects of a large asteroid impact leave deep and lasting scars on both the natural environment and human communities at the level of an extinction level event. Although the probability of such a disaster is low, given its possible consequences, scientists and governments continue to look for ways to be prepared for such a scenario. Studies carried out to detect meteorite collisions in advance and minimize their effects show that humanity is not defenseless against such disasters. In this context, international cooperation and scientific research play a critical role in the security of the Earth. Of course, there may be serious effects depending on where the meteorite hits, and the countries where it hits may be at greater risk depending on the size of the meteorite. So, how ready are we for such a possibility and what kind of plans we have as a nation, these should always be reviewed and prepared. You can learn more at Aerospace Lectures in Astronautics tab.
























Add Comment